According to the Finance Minister of India, the Union Budget builds on the foundations laid in the previous budget and presents a blueprint of what India should be in the 100th year of its independence. The objective is to make the fruits of development reach all regions and citizens. This goal is set in the backdrop of the recent economic performance indicators of the Indian economy which is being considered as a ‘bright star’ in an otherwise gloomy economic environment in the global economy. Also, according to the economic survey 2022-23, the current year’s economic growth is estimated to be at 7 per cent making India the fastest growing economy in the world.

Vision– an empowered and inclusive economy
The vision is to steer through a technology-driven and knowledge-based economy with strong public finances, and a robust financial sector. The economic agenda for achieving this vision focuses on three things:
- facilitating ample opportunities for citizens, especially the youth, to fulfil their aspirations;
- providing strong impetus to growth and job creation; and
- strengthening macro-economic stability.

Priorities of the Budget 2023-24
The Budget adopts the following seven priorities (named as ‘Saptarishi’ ) which complement each other and together would act as the guiding force for the Budget’s development strategy:
- Inclusive Development
- Reaching the Last Mile
- Infrastructure and Investment
- Unleashing the Potential
- Green Growth
- Youth Power
- Financial Sector
This seven pronged development strategy is briefly discussed below:
Priority 1: Inclusive Development
The Budget reiterates the focus on the Government’s philosophy of ‘Sabka Saath Sabka Vikas’ and lists out numerous inclusive development initiatives taken by it:

Priority 2: Reaching the Last Mile
The second priority is to ‘reach the last mile’ through the policies and programs initiated by ministries of Tribal Affairs, AYUSH, Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying, Skill Development, Jal Shakti and Cooperation and the Department of Development of North-Eastern Region. The highlights are as below:

Priority 3: Infrastructure & Investment
The Budget focus is on boosting the virtuous cycle of investment and job creation.

Priority 4: Unleashing the Potential
The budget proposes to provide a transparent and accountable administration which works for the betterment and welfare of the common citizen:

Priority 5: Green Growth
The budget intends to promote an environmentally conscious lifestyle and achieve net-zero carbon emission by 2070 to usher in green industrial and economic transition:

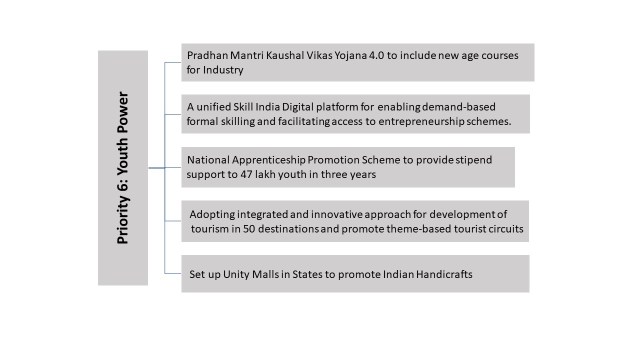
Priority 6: Youth Power
Formulation of the National Education Policy, focused on skilling, adopted economic policies that facilitate job creation at scale, and have supported business opportunities:
Priority 7: Financial Sector
The reforms in the financial sector and innovative use of technology have reportedly led to financial inclusion at scale, better and faster service delivery, ease of access to credit and participation in financial markets. The Budget proposes to further these measures.

Fiscal Management
- The budget provides for fifty-year loan to states exclusively for the purpose of incurring capital expenditure within 2023-24 mostly at the discretion of states, but a part will be conditional on states increasing their actual capital expenditure and allocating part of the outlay for the designated purposes.
- The budget sets a limit on the fiscal deficit of the states which shall be 3.5 per cent of GSDP of which 0.5 per cent will be tied to power sector reforms.
- The revised estimate for fiscal deficit for the current financial year is 6.4 per cent of GDP which is quite in line with the budget estimate.
- The fiscal deficit is estimated to be 5.9 per cent of GDP in the coming financial year 2023-24.
Reference: This article is published by the Author in the Newsletter “KnowFunda Digest” (6th Edition) on LinkedIn on February 9, 2023.